Are you seeing spots or flashes? Eye flashes and floaters are common visual disturbances that can appear as small, drifting specks or sudden bursts of light in your field of vision. Floaters are tiny clumps of collagen within the vitreous gel that cast shadows on the retina, while flashes occur when the vitreous pulls on the retina, triggering brief streaks of light. While these symptoms are usually harmless, a sudden increase in floaters or flashes could indicate a retinal tear or detachment, which requires immediate medical attention. At Eye Care Specialists of Michigan, we use advanced diagnostic tools to assess your eye health and determine if treatment is necessary to protect your vision. If you’re experiencing new or worsening flashes or floaters, schedule an eye exam to ensure your retina is healthy.
What are Eye Floaters?
Eye floaters are small, shadowy shapes that drift across your vision, often appearing as spots, squiggles, or cobweb-like strands. They are caused by tiny clumps of collagen fibers floating in the vitreous gel inside the eye. While generally harmless, a sudden increase in floaters—especially when accompanied by flashes—may indicate a serious retinal issue that needs prompt evaluation.
What are Eye Flashes?
Eye flashes appear as sudden, brief bursts or streaks of light in your vision, similar to a camera flash or lightning strike. They occur when the vitreous gel inside the eye pulls or tugs on the retina, stimulating light-sensitive cells. While occasional flashes can be normal, frequent or new flashes may signal a retinal tear or detachment, requiring immediate medical attention.
Causes of Floaters & Flashes
Nearsightedness
Eye Surgery
Diabetes
Injury to the Eye
Cataracts
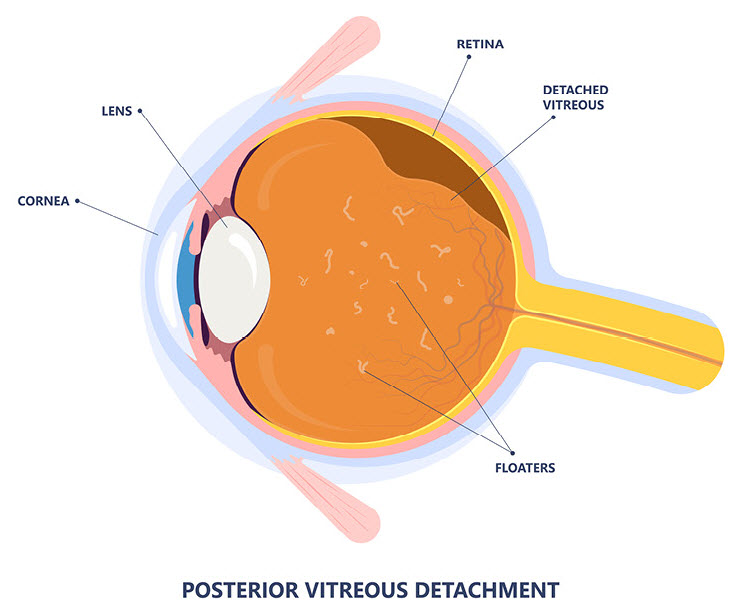
Occasional eye floaters and flashes are common and usually harmless, often appearing briefly before fading. They may be more noticeable in the morning, while reading, or after rubbing your eyes. However, frequent or persistent flashes and floaters could indicate posterior vitreous detachment (PVD)—a natural age-related change in the eye. While floaters and flashes typically result from the breakdown of collagen in the vitreous humor, PVD occurs when the vitreous gel starts to separate from the retina. Although PVD is usually not serious, a sudden increase in symptoms should be evaluated by an eye care specialist to rule out retinal complications.
When to Seek Treatment
While occasional eye flashes and floaters are normal, a sudden increase in their frequency, size, or intensity could signal a more serious issue, such as a retinal tear or detachment. If you experience a sudden shower of floaters, persistent flashes of light, a shadow or curtain effect in your vision, or any loss of peripheral vision, seek immediate medical attention.
At Eye Care Specialists of Michigan, our team uses advanced diagnostic technology to assess your eye health and provide the best course of treatment to protect your vision. If you’re experiencing new or worsening flashes and floaters, don’t wait—schedule an eye exam today.





